Partner 3
Physiopathology and epidemiology of respiratory diseases
Director of partner
marina.petrolani@inserm.fr - 0157277586Research areas :
L’Inserm UMR1152 étudie les facteurs de risque et les mécanismes cellulaires et moléculaires impliqués dans la survenue et la progression des maladies respiratoires, en particulier, l’asthme, la bronchopneumopathie bronchique obstructive (BPCO) et les fibroses pulmonaires, soit idiopathiques (FPI), soit associées aux lésions pulmonaires aigues (‘acute lung injury’, ALI, et le syndrome de détresse respiratoire aigu, SDRA). Des approches cliniques, épidémiologiques et de recherche fondamentale sont utilisées pour déterminer l’origine de ces maladies et de l’inflammation et la fibrose tissulaires qui les accompagnent. Un intérêt particulier est porté sur (i) l’analyse des mécanismes impliqués dans la perte de l’intégrité de l’épithélium respiratoire et dans les anomalies du processus de réparation, et (ii) sur l’étude de l’origine des fibroblastes pulmonaires (transition épithélio-mésenchymateuse, différenciation à partir de fibrocytes ou en myofibroblastes) et dans leurs altérations fonctionnelles (survie/apoptose, migration, prolifération).
Partner 3 hosts 4 research teams:
Team 1 – Respiratory Epidemiology: from the ethilogy of Asthma and BPCO to prognosis of lung transplantion
Contact : Pr Gabriel Thabut (gabriel.thabut@bch.aphp.paris.fr / 01.40.25.69.12)
Team 2 – Inflammation and bronchiolar remodeling in obstructive pulmonary pathologies
Contact : Dr Marina Pretolani (marina.pretolani@inserm.fr / 01.57.27.75.86) et Pr Michel Aubier (michel.aubier@bch.aphp.fr / 01.40.25.68.00)
Team 3 – Inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis
Contact : Pr Bruno Crestani (bruno.crestani@bch.aphp.paris.fr / 01.40.25.86.86)
Team 4 – Innate immunity and anti-infective pulmonary defences
Research themes :
Three main areas of investigation are currently being pursued in our team :
1) Study in vitro and in vivo of the role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections (an opportunistic pathogen in pulmonary nosocomial infection and in cystic fibrosis) in exacerbations of chronic lung diseases, including cystic fibrosis.
2) In 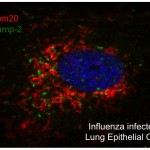 vitro and in vivo study of the mechanisms through which Influenza virus, a pathogen responsible for lung infections in seasonal flu or pandemic episodes can favour bacterial super-infections and induce disease exacerbations in chronic lung diseases.
vitro and in vivo study of the mechanisms through which Influenza virus, a pathogen responsible for lung infections in seasonal flu or pandemic episodes can favour bacterial super-infections and induce disease exacerbations in chronic lung diseases.
3) Inv estigation of the molecular mechanisms of action of nanoparticles in the lung, in isolation or in conjunction with lung pathogens (S. aureus, P.aeruginosa, Influenza virus…).
estigation of the molecular mechanisms of action of nanoparticles in the lung, in isolation or in conjunction with lung pathogens (S. aureus, P.aeruginosa, Influenza virus…).
The molecular processes, techniques, reagents, signalling pathways studied and used in this context include :
-mechanisms of Pathogen Associate Molecular Pattern/PAMP receptors activation, phagocytic processes, signal transduction pathways ; role of epithelial type 2 serine proteases (TTSPs) during Influenza infection ; interactions between microbial virulence factors, innate immune receptors and epithelial channels (eg le CFTR) ; study of endogenous antimicrobial molécules ; use of recombinant adenovirus vectors in over-expression protocols ; invivo rodent infection models ; RT-qPCR ; flow cytometry ; immuno-histochemistry ; proteomics.
Teaching : Master Infectiologie, Master Inflammation, Université Paris Diderot
Recent publications :
– Saint-Criq V, Villeret B, Bastaert F, Kheir S, Hatton A, Cazes A, Xing Z, Sermet-Gaudelus I, Garcia-Verdugo I, Edelman A, Sallenave JM. Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasB protease impairs innate immunity in mice and humans by targeting a lung epithelial cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator-IL-6-antimicrobial-repair pathway. Thorax. 2017 Aug 8. pii: thoraxjnl-2017-210298.
– Lim AI, Li Y, Lopez-Lastra S, Stadhouders R, Paul F, Casrouge A, Serafini N, Puel A, Bustamante J, Surace L, Masse-Ranson G, David E, Strick-Marchand H, Le Bourhis L, Cocchi R, Topazio D, Graziano P, Muscarella LA, Rogge L, Norel X, Sallenave JM, Allez M, Graf T, Hendriks RW, Casanova JL, Amit I, Yssel H, Di Santo JP. Systemic Human ILC Precursors Provide a Substrate for Tissue ILC Differentiation.Cell. 2017 ;168:1086-1100.e10.
-Roussilhon C, Bang G, Bastaert F, Solhonne B, Garcia-Verdugo I, Peronet R, Druilhe P, Sakuntabhai A, Mecheri S, Sallenave JM. The antimicrobial molecule trappin-2/elafin has anti-parasitic properties and is protective in vivo in a murine model of cerebral malaria.Sci Rep. 2017;7:42243.
-Delaval M, Boland S, Solhonne B, Nicola MA, Mornet S, Baeza-Squiban A, Sallenave JM, Garcia-Verdugo I.Acute exposure to silica nanoparticles enhances mortality and increases lung permeability in a mouse model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2015 Jan 21;12:1. doi: 10.1186/s12989-014-0078-9.
-Brown TI, Collie DS, Shaw DJ, Rzechorzek NM, Sallenave JM. –Sheep lung segmental delivery strategy demonstrates adenovirus priming of local lung responses to bacterial LPS and the role of elafin as a response modulator.PLoS One. 2014;9:e107590
-Le Gars M, Descamps D, Roussel D, Saussereau E, Guillot L, Ruffin M, Tabary O, Hong SS, Boulanger P, Paulais M, Malleret L, Belaaouaj A, Edelman A, Huerre M, Chignard M, Sallenave JM. Neutrophil elastase degrades cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator via calpains and disables channel function in vitro and in vivo. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:170-9.
-Drannik AG, Nag K, Sallenave JM, Rosenthal KL. Antiviral activity of trappin-2 and elafin in vitro and in vivo against genital herpes.J Virol. 2013;87:7526-38.
-Descamps D, Le Gars M, Balloy V, Barbier D, Maschalidi S, Tohme M, Chignard M, Ramphal R, Manoury B, Sallenave JM. Toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5), IL-1β secretion, and asparagine endopeptidase are critical factors for alveolar macrophage phagocytosis and bacterial killing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:1619-24.
–Garcia-Verdugo I, BenMohamed F, Tattermusch S, Leduc D, Charpigny G, Chignard M, Ollero M, Touqui L. A A role for 12R-lipoxygenase in MUC5AC expression by respiratory epithelial cells. Eur Respir J. 2012 ;40:714-23
-Ehre C, Worthington EN, Liesman RM, Grubb BR, Barbier D, O’Neal WK, Sallenave JM, Pickles RJ, Boucher RC. Overexpressing mouse model demonstrates the protective role of Muc5ac in the lungs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:16528-33
-Motta JP, Magne L, Descamps D, Rolland C, Squarzoni-Dale C, Rousset P, Martin L, Cenac N, Balloy V, Huerre M, Jenne D, Wartelle J, Belaaouaj A, Mas E, Vinel JP, Alric L, Chignard M, Vergnolle N, Sallenave J-M. Modifying the Protease, Antiprotease Pattern by Elafin Overexpression Protects Mice From Colitis.
Gastroenterology. 2011; 140:1272-82
Contact: Pr Jean-Michel Sallenave :
Tel : +33157277802
Fax : +33157277551
e-mail : jean-michel.sallenave@inserm.fr
Fiche Aviesan ITMO ‘PMN’ : https://pmn.aviesan.fr/index.php?pagendx=295&team=279
Current team members :
-Pr J-M Sallenave, PU CE, Université Paris-Diderot
-Dr I. Garcia-Verdugo, MCU, Université Paris-Diderot
-Pr P. Montravers, PU-PH, Hôpital Bichat.
-Pr A. Khalil, PU-PH, Hôpital Bichat.
-Mrs B. Villeret, IE, Université Paris-Diderot.
-Mrs R. Ghinnagow, Post-doctoral fellow, INSERM.
-Mrs A. Picart, tech., INSERM.
-Mr S. Kheir, PhD student, Université Paris-Diderot
-Mr P. Leguen, M2 student, Université Paris-Diderot
-Mr D. Sanchez, M2 student, Université Paris-Diderot



